Gum Disease (Periodontics)
Do you notice bleeding when you brush or floss your teeth? Are your gums swollen, red or tender? You might be developing what is commonly addressed as gum disease or Gingivitis.
Gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease, is inflammation of the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth and is most commonly a result of poor dental hygiene. Gingivitis is a very common condition and varies widely in severity. Gingivitis always precedes and acts as a warning sign for the more serious condition of periodontitis.
Gingivitis starts when food debris mixes with saliva and bacteria which, in turn, forms dental plaque that sticks to the surfaces of teeth. If dental plaque isn’t removed by brushing with toothpaste and flossing, it can become mineralized and form tartar, or calculus. Tartar is very hard, and only a professional dental cleaning can remove it.
FAQ
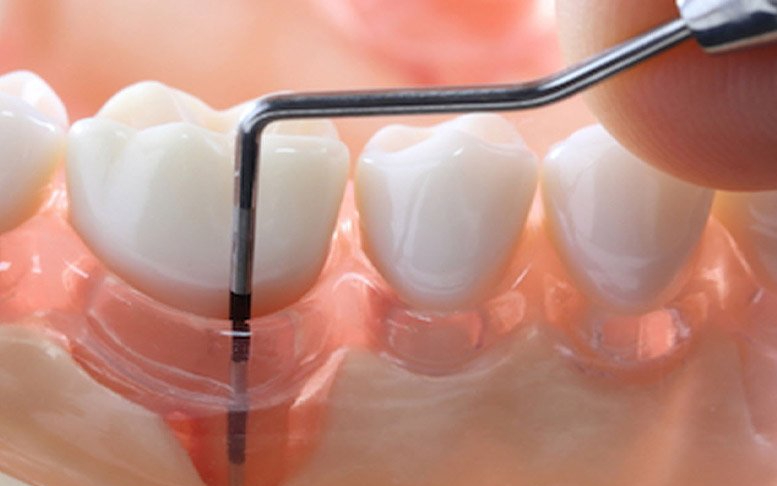
Gingivitis, or early gum disease, often produces symptoms such as red, tender gums and bleeding while flossing. You also might notice bleeding while eating hard or crunchy foods. Your dental hygienist might tell you that you have some pockets in your gums where they attach to your teeth.
As gum disease progresses, it can turn to periodontitis. Symptoms are more severe than those found with gingivitis. Pockets will get larger and you might notice pus seeping out between your gums and your teeth. Your teeth might get loose. You might get sores in your mouth or struggle with a foul taste or smell coming from your mouth.
Periodontitis can cause tooth loss and serious infections. In rare cases, the infection can spread. There are also indications that dental infections can cause heart problems or exacerbate the symptoms of diabetes.
Causes include smoking and poor dental hygiene. There are also risk factors you might not be able to control, such as genetics, age and underlying diseases like diabetes or heart disease.
Your Dentist will first instruct you in good oral hygiene. In cases of mild gingivitis, improving your dental hygiene can actually reverse the condition and improve the health of your gums. If the disease has progressed to periodontitis, treatments might include scaling and root planing, laser treatment, and various surgical treatments.
Having excellent oral hygiene and seeing your dentist regularly can help prevent gum disease. Quit smoking if you currently smoke. Let your dentist know what medications you are on because some drugs can cause gum inflammation. Finally, follow your dentist’s recommendations when it comes to keeping your gums and teeth healthy.